In the world of digital marketing, businesses often hear about SEO, PPC, and GEO targeting. While they all aim to improve online visibility, each works differently.
Understanding the difference between SEO, PPC, and GEO helps marketers choose the right strategy, attract the right audience, and maximize their return on investment. This article breaks down each method, its advantages, and how they can work together.
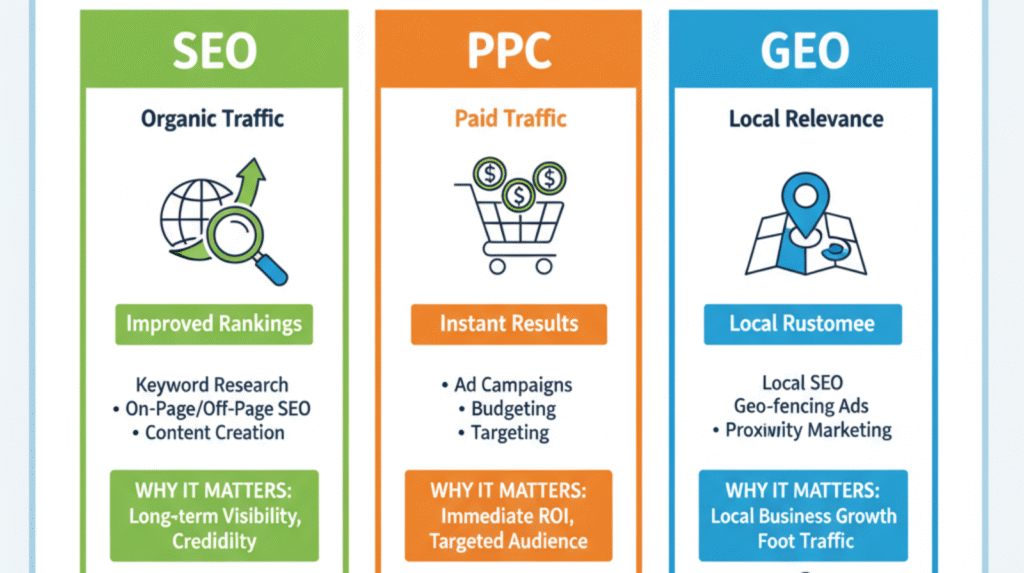
1. What Is SEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) focuses on increasing organic, unpaid traffic from search engines. Instead of paying for each visitor, you optimize your website so that it appears naturally in search results.
How SEO Works
Adding relevant keywords naturally into content
Creating high-quality, original content
Optimizing site speed, mobile usability, and navigation
Building trustworthy backlinks from other websites
Example:
A local bakery can use SEO to appear for searches like “fresh cakes near me,” attracting customers without paying for ads.
Why Use SEO
Long-term, sustainable traffic
Builds trust and brand credibility
Cost-effective over time
Helps improve overall website authority
2. What Is PPC?
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is a paid advertising method. You pay a fee whenever someone clicks on your ad. Platforms such as Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and Instagram Ads are commonly used for PPC campaigns.
How PPC Works
Choose the keywords related to your product or service
Set a daily or monthly budget for the campaign
Display ads at the top of search results or social feeds
Pay only when someone clicks your ad
Example:
A skincare brand can use PPC to appear for “buy moisturizer online” and instantly reach potential customers without waiting for organic SEO results.
Why Use PPC
Immediate results and visibility
Easy to track performance and ROI
Great for promotions, product launches, or seasonal campaigns
] Allows precise targeting based on demographics or interests
3. What Is GEO Targeting?
GEO targeting allows you to deliver content, ads, or promotions to users in a specific geographic location, such as a city, state, or country.
How GEO Works
Define the target area where your audience is located
Show your ads only to users in that area
Tailor content to local interests or cultural preferences
Example:
A coffee shop in Karachi can use GEO targeting so only people in Karachi see ads for their promotions.
Why Use GEO Targeting
Reaches the most relevant audience
Improves conversion rates
Reduces wasted ad spend
Supports local marketing campaigns
4. Key Differences Between SEO, PPC, and GEO
| Feature | SEO | PPC | GEO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Organic | Paid | Location-based |
| Cost | Free clicks | Pay per click | Optional (used with SEO/PPC) |
| Speed | Slow, long-term | Fast, immediate | Depends on setup |
| Best For | Sustainable traffic | Quick sales or leads | Local or region-specific targeting |
| Result Duration | Long-lasting | Short-term | Ongoing if maintained |
5. How They Work Together
The most effective digital marketing strategy combines all three:
SEO builds authority and long-term organic traffic.
PPC provides instant visibility and leads.
GEO targeting ensures you reach the right audience based on location.
Example:
A gym can optimize its website with SEO for “fitness center near me,” run PPC ads for new membership offers, and use GEO targeting to show ads only in the city where the gym is located.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between SEO, PPC, and GEO is crucial for businesses aiming to grow online.
SEO gives long-term, unpaid traffic.
PPC delivers instant, paid traffic with measurable results.
GEO targeting ensures location-specific marketing.
Used together, these strategies create a strong, comprehensive marketing system that increases visibility, drives traffic, and improves conversions.